| 1. | What are STP and SATP? Give definitions and appropriate values. | |||
| 2. | Identify each of the following reactions as endothermic or exothermic. Also, write each one in an equivalent way. |
|||
|
||||
| A. | 2 Hg(l) + I2 (s) → Hg2I2 (s) ΔH ° = -28.9 kcal | |||
| B. | N2 (g) + 3 F2 (g) → 2 NF3 (g) + 27.2 kcal | |||
| C. | NH4NO3 (s) + 6.1 kcal → NH4+(aq) + NO3-(aq) | |||
| D. | Na(s) → Na(g) ΔH ° = 25.98 kcal | |||
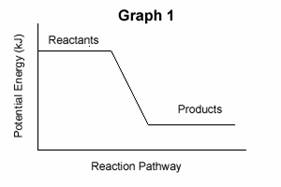
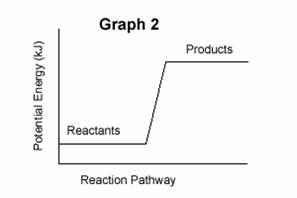
| 3. | Consider the following two potential energy graphs: | |||
| A. | Identify the following graphs as representing endothermic or exothermic reactions: | |||
 |
 |
|||
| B. | Which graph above will have a value for ΔH that is negative ? | |||
| 4. | Using a table of thermochemical data, write heats of formation reactions for the following compounds. Include the energy term as part of the equation. | |||
|
||||
| A. | SO2 (g) | |||
| B. | C3H8 (g) | |||
| C. | N2O(g) | |||
| D. | Na2CO3 (s) | |||
| 5. | On the basis on energy changes, select the three reactions from the list below that are most likely to occur spontaneously: | |||
| A. | H2 (g) + O2 (g) → H2O(g) + 220.1 kJ | |||
| B. | 3 CO2 (g) + 4 H2O(l) + 2220 kJ → C3H8 (g) + 5 O2 (g) | |||
| C. | 2 HCl(g) → H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) ΔH ° = +185 kJ | |||
| D. | CH4 (s) + 2 O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + 2 H2O(l) ΔH ° = -890 kJ | |||
| E. | 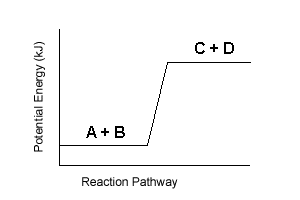 |
|||
| F. | 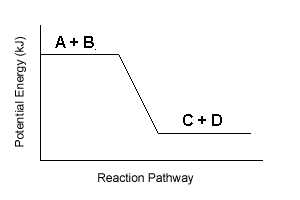 |
|||
Chemistry 30
Thermodynamics: Unit Index | Practice Problems | Assignments
| Student Lab | Research Ideas | Teacher Resources
Kinetics: Unit Index | Practice Problems | Assignments
| Student Lab | Research Ideas | Teacher Resources
Equilibrium: Unit Index | Practice Problems | Assignments
| Student Lab | Research Ideas | Teacher Resources
Solutions: Unit Index | Practice Problems | Assignments
| Student Lab | Research Ideas | Teacher Resources
Acids & Bases: Module Index | Practice Problems | Assignments
| Student Lab | Research Ideas | Teacher Resources
Redox Reactions: Module Index | Practice Problems | Assignments
| Student Lab | Research Ideas | Teacher Resources