| 1. | Consider the following reaction that occurs between hydrochloric acid, HCl, and zinc metal: HCl(aq) + Zn(s) → H2 (g) + ZnCl2 (aq) Will this reaction occur fastest using a 6 M solution of HCl or a 0.5 M solution of HCl? Explain. |
||||
| 2. | Again consider the reaction between hydrochloric acid and zinc. How will increasing the temperature affect the rate of the reaction? Explain. |
||||
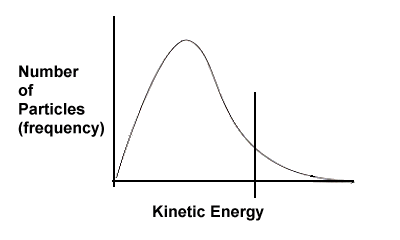
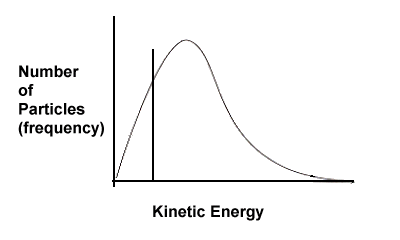
| 3. | Based on the following kinetic energy curves, which reaction will have a faster rate - A or B? Explain. Also, which reaction, A or B, would benefit most in terms of increased rate if the temperature of the system were increased? | ||||
|
Chemistry 30
Thermodynamics: Unit Index | Practice Problems | Assignments
| Student Lab | Research Ideas | Teacher Resources
Kinetics: Unit Index | Practice Problems | Assignments
| Student Lab | Research Ideas | Teacher Resources
Equilibrium: Unit Index | Practice Problems | Assignments
| Student Lab | Research Ideas | Teacher Resources
Solutions: Unit Index | Practice Problems | Assignments
| Student Lab | Research Ideas | Teacher Resources
Acids & Bases: Module Index | Practice Problems | Assignments
| Student Lab | Research Ideas | Teacher Resources
Redox Reactions: Module Index | Practice Problems | Assignments
| Student Lab | Research Ideas | Teacher Resources